(Leetcode) 322 - Coin Change 풀이
New Year Gift - Curated List of Top 75 LeetCode Questions to Save Your Time
위 링크에 있는 추천 문제들을 시간이 있을때마다 풀어보려고 한다.
https://leetcode.com/problems/coin-change/description/
DP 문제이다.
내가 풀었던 방식
처음 생각
처음에는 큰 동전부터 넣어서 될 때까지 하면 베스트 일 것이라고 생각했다. 하지만 그렇게 간단하지는 않았다.
예를들어 [100, 30, 1] 이라는 동전이 있다고 해보자. 이때 주어지는 amount는 120 이라고 하면
30으로는 4개면 되지만 100을 먼저 채우면 30은 들어갈 수 없고 1짜리 20개를 더 써서 21개의 동전이 사용된다.
중간 생각
그래서 모든 경우의 수를 다 찾아봐야 겠다고 생각했다. 처음에는 잘 먹히는 듯 보였으나, 역시나 복잡한 경우로 인해 타임아웃이 발생되었다.
class Solution:
def coinChange(self, coins: List[int], amount: int) -> int:
if amount == 0:
return 0
coins.sort()
coins.reverse()
stack = []
worst = math.floor(amount / coins[-1])
min = worst + 1
def calc(index, amount):
nonlocal min
# print("start:", stack, len(stack), amount, index)
if len(stack) == worst:
return -1 if min > worst else min
while index == len(coins):
last_removed_index = stack.pop()
amount += coins[last_removed_index]
index = last_removed_index + 1
while amount > 0:
stack.append(index)
amount -= coins[index]
if amount == 0:
if min > len(stack):
min = len(stack)
# print("min:", min)
removed_index = stack.pop()
amount += coins[removed_index]
return calc(removed_index + 1, amount)
try:
return calc(0, amount)
except:
return min
모범 답안
모든 시점에서의 최선을 상황을 찾는다.
from typing import List
import math
class Solution:
def coinChange(self, coins: List[int], amount: int) -> int:
dp = [0] + ([float('inf')] * amount)
for i in range(1, amount + 1):
for coin in coins:
if coin <= i:
dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[i - coin] + 1)
if dp[-1] == float('inf'):
return -1
return dp[-1]
예시를 들어 차근차근 실행시켜보기
for 문의 끝에 아래와 같이 print를 넣어주면 다음과 같이 print 된다.
print(solution.coinChange([1, 2, 5], 10))
[0, 1, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf] 1
[0, 1, 1, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf] 2
[0, 1, 1, 2, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf] 3
[0, 1, 1, 2, 2, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf] 4
[0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf] 5
[0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2, inf, inf, inf, inf] 6
[0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, inf, inf, inf] 7
[0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 3, inf, inf] 8
[0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, inf] 9
[0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 2] 10
풀어서 설명하면 다음과 같다.





시간복잡도
- 이중 반복문 사용
- 바깥쪽 반복문 : amount 만큼 반복 (O(n))
- 안쪽 반복문 : coins 리스트의 length 만큼 반복 (O(m))
O(n * m) 의 시간 복잡도를 가짐
공간복잡도
amount 만큼 dp array를 생성함
O(n) 의 공간 복잡도를 가짐
결론
DP 문제를 더 많이 접해봐야겠다는 생각이 들었다.
java 로 다시 풀기 (24.07.09)
먼저는 stream으로 풀었다. 이미 들린 dp pointer 일 때, 기존에 등록된 값보다 클 경우 (dp[currentPointer] > dp[amount] + 1) 이후 dfs 단계를 생략하도록 한 것이 포인트이다.
처음으로 dp[0]에 도달했다고 해서 최소값이 아니기 때문에 전체 케이스를 고려해야 하는데 그렇다고 진짜로 전체 케이스를 확인해본다면 timeout이 발생된다. 따라서 이 조건문을 찾아내지 못하면 timeout이 발생된다.
class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
if(amount == 0) {
return 0;
}
int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
List<Integer> sortedCoins = Arrays.stream(coins).boxed()
.sorted(Collections.reverseOrder())
.toList();
sortedCoins.forEach(coin -> dfs(dp, sortedCoins, amount, coin));
return dp[0] == 0 ? -1 : dp[0];
}
void dfs(int[] dp, List<Integer> coins, int amount, int selectedCoin) {
int currentPointer = amount - selectedCoin;
if (currentPointer < 0) {
return;
}
if (dp[currentPointer] == 0 || dp[currentPointer] > dp[amount] + 1) {
dp[currentPointer] = dp[amount] + 1;
coins.forEach(coin -> dfs(dp, coins, currentPointer, coin));
}
}
}
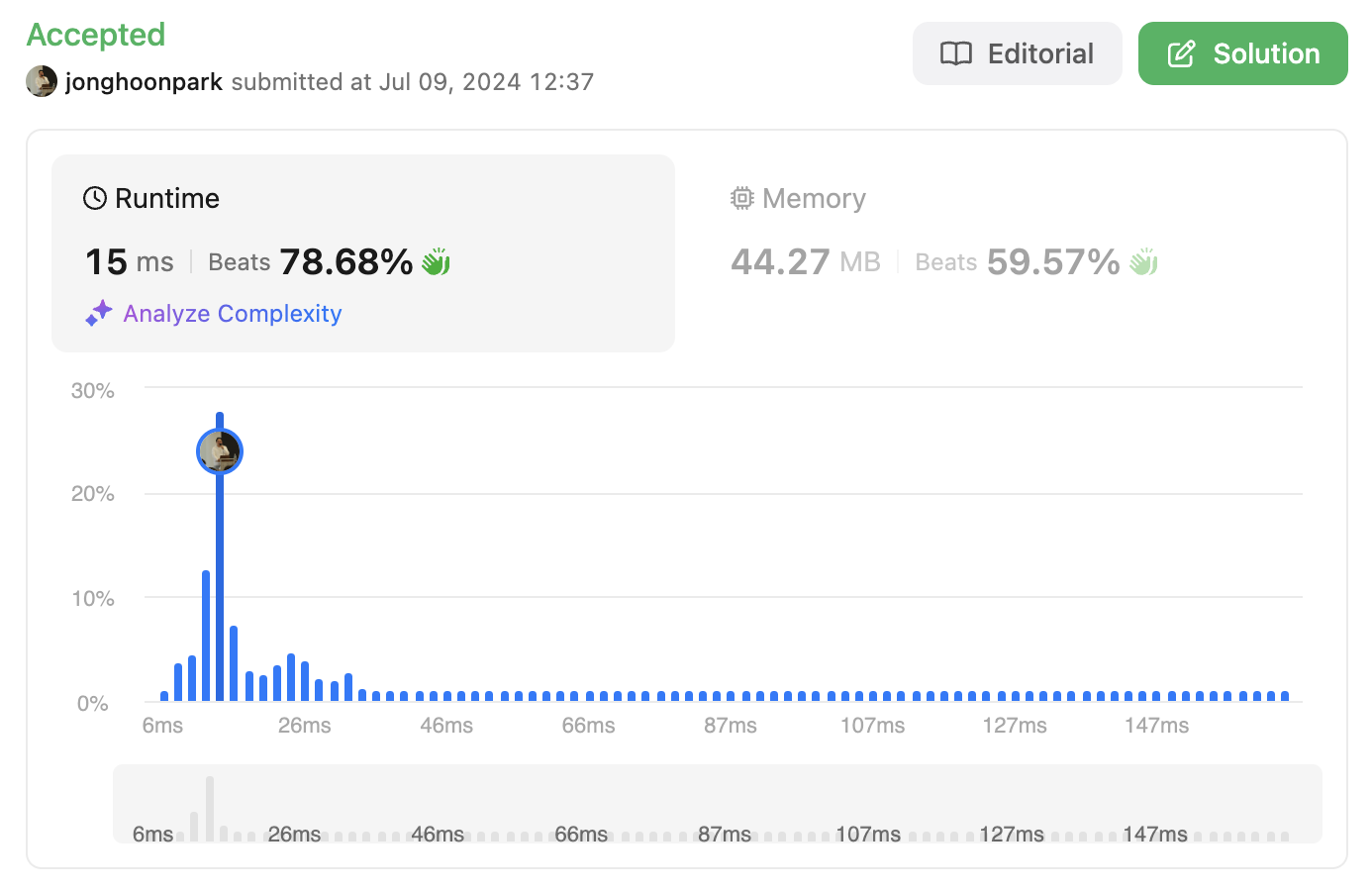
stream 의 경우 for loop 보다는 느리지만 이해하기에는 훨씬 좋다. 더 직관적이다.
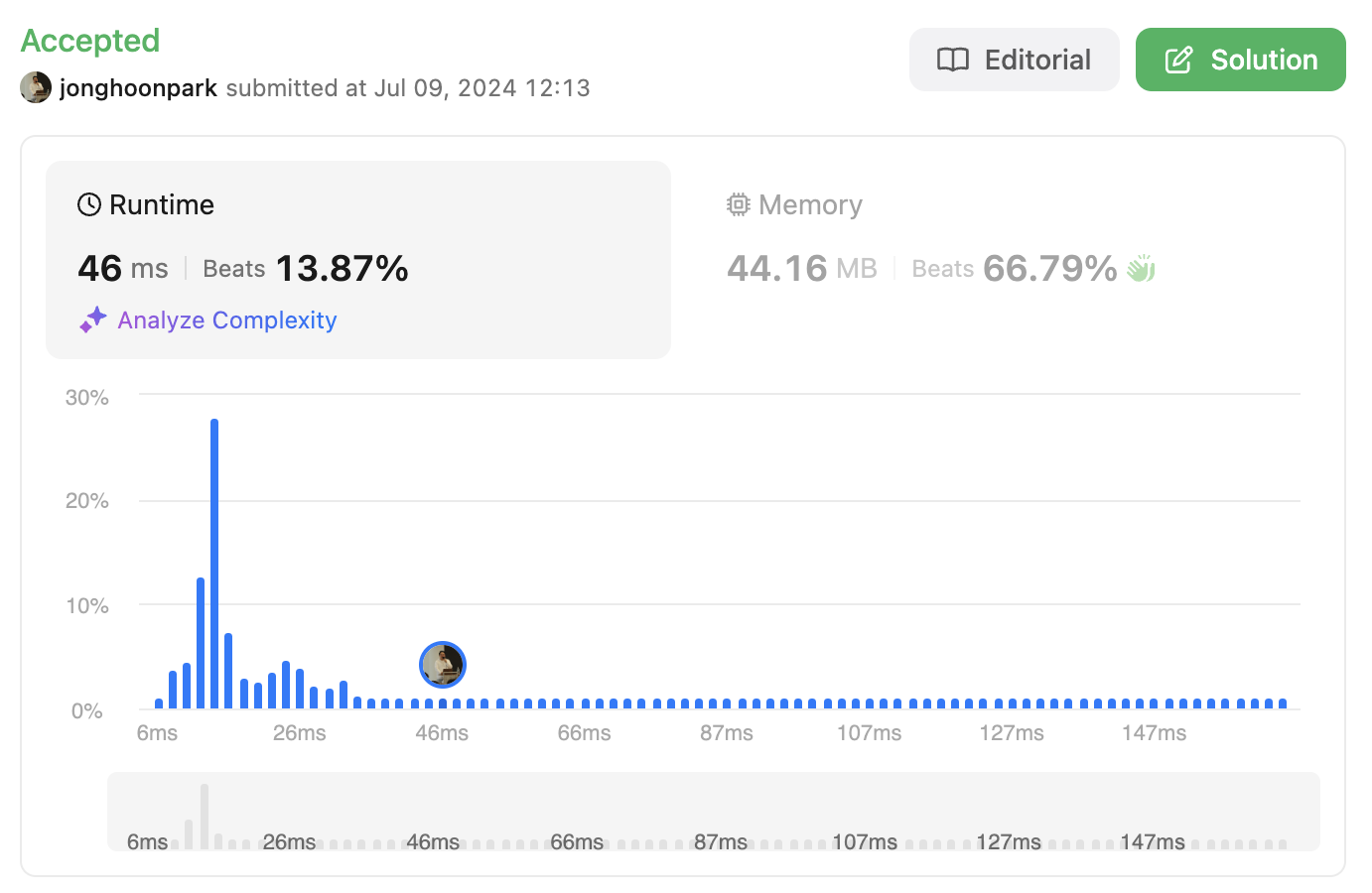
다만 성능을 더 최적화 하기 위해서 for loop를 이용해서 풀도록 바꾸면 다음과 같다.
class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
if(amount == 0) {
return 0;
}
int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
Arrays.sort(coins);
for (int i = coins.length - 1; i > -1; i--) {
dfs(dp, coins, amount, coins[i]);
}
return dp[0] == 0 ? -1 : dp[0];
}
void dfs(int[] dp, int[] coins, int amount, int selectedCoin) {
int currentPointer = amount - selectedCoin;
if (currentPointer < 0) {
return;
}
if (dp[currentPointer] == 0 || dp[currentPointer] > dp[amount] + 1) {
dp[currentPointer] = dp[amount] + 1;
for (int i = coins.length - 1; i > -1; i--) {
dfs(dp, coins, currentPointer, coins[i]);
}
}
}
}

stream을 사용했을 때보다 시간이 단축된 것을 볼 수 있다.
TS, SC
코인의 수를 n 이라고 했을 때, O(n * amount ^ 2) 의 시간복잡도와 O(amount) 의 공간복잡도를 가진다.
java 모범 답안 (더 효율적인 방법)
위 코드는 dp 라는 array를 사용하긴 했지만, 사실 brute force 에 가까운 방법이다.
아래와 같이 작성하면 더 효율적으로 동작한다.
public class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int max = amount + 1;
int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
Arrays.fill(dp, max);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < coins.length; j++) {
if (coins[j] <= i) {
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - coins[j]] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[amount] > amount ? -1 : dp[amount];
}
}
TS, SC
코인의 수를 n 이라고 했을 때, O(n * amount) 의 시간복잡도와 O(amount) 의 공간복잡도를 가진다.